转录组数据处理笔记 一、前置环境 1.1 Linux子系统 首先肯定是在Linux上进行,我这边稍微记录一下现在装Linux子系统的步骤:
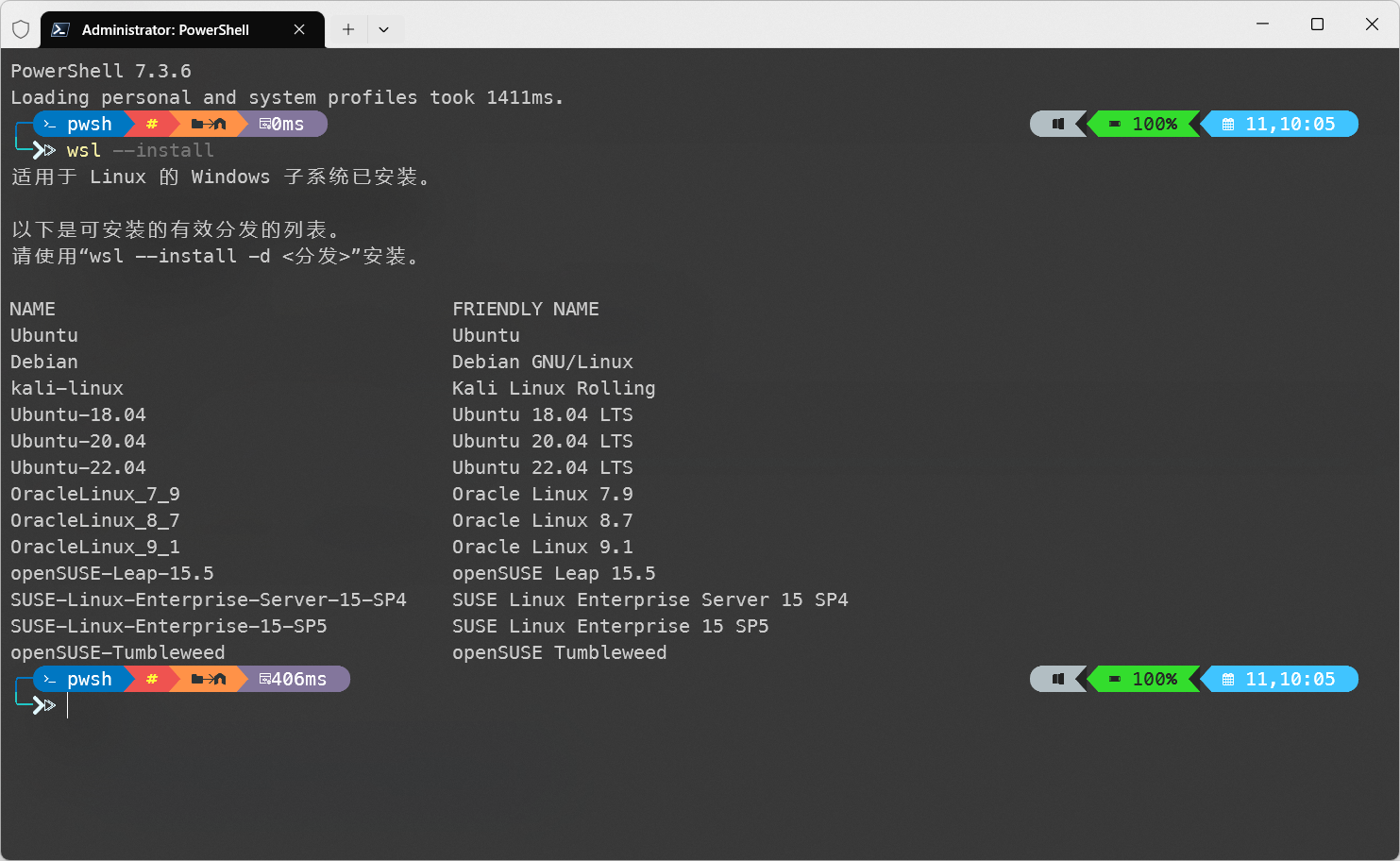
以管理员模式运行Windows terminal,并执行以下指令:
安装完毕后,再次运行此指令,能够看到如下界面:
wsl分支 接下来根据提示,安装指定的分支,例如我选择Ubuntu22:
1 wsl --install -d Ubuntu-22 .04
运行期间会要求输入用户名密码等,跟着输入就行。
当使用完子系统之后,直接关闭窗口并不会结束子系统进程,这会导致其依然在系统内存中占用资源。
想要彻底关闭WSL,在power shell中执行以下指令:
1.2 conda安装及镜像配置 首先安装miniconda,下载安装脚本,并赋予其相应权限,之后运行脚本即可:
1 2 3 wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-py310_23.5.2-0-Linux-x86_64.shchmod 777 Miniconda3-py310_23.5.2-0-Linux-x86_64.sh
具体文件名字视你下的版本而定
脚本运行期间,基本上是一路yes到底就行了。
conda安装完毕之后,重启系统或者通过一下指令刷新环境变量:
接下来配置所使用的镜像,这里需要使用bioconda这个channel:
1 2 conda config --set show_channel_urls yes
将配置文件修改如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 channels: - defaults show_channel_urls: true default_channels: - https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main - https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/r - https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/msys2 - https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/conda-forge - https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/bioconda custom_channels: conda-forge: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud msys2: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud bioconda: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud menpo: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud pytorch: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud pytorch-lts: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud simpleitk: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud deepmodeling: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/
之后使用如下指令来清空缓存:
现在可以创建一个新的环境了:
1 2 conda create --name bioinfo python=3.10
二、质量分析 这里所使用到的软件为fastqc与multiqc,这俩其实用处差不多,只不过后者可以将多份数据进行整合。
2.1 软件安装 直接通过conda安装即可:
1 conda install fastqc multiqc
2.2 参数含义 FastQC -h 或 --help :显示帮助信息-o <output_dir> 或 --outdir <output_dir>:指定输出目录,将生成的结果文件保存到指定的目录中-f <format> 或 --format <format>:指定输入文件的格式。常见的格式包括"fastq"、"bam"、"sam"等-t <threads> 或 --threads <threads>:指定线程数,用于加速分析。默认为1个线程-c <config_file> 或 --config <config_file>:指定配置文件,配置额外的参数等-k <kmersize> 或 --kmersize <kmersize>:指定用于检测存在的最大k-mer大小。默认为10-adapters <adapters_file>:指定adapter序列文件,用于adapter污染检测-limits <limits_file>:指定limits文件,用于制定可接受的范围,例如序列长度、GC含量等-extract:提取原始的FastQC zip文件,而不进行分析-q 或 --quiet:静默模式,只输出错误消息MultiQC -h 或 --help :显示帮助信息。-o <output_dir> 或 --outdir <output_dir>:指定输出目录,将生成的报告文件保存到指定的目录中。-c <config_file> 或 --config <config_file>:指定配置文件,自定义报告生成的规则和设置。-s 或 --fullnames:显示完整的样本名称,而不仅仅是文件名部分。--title <report_title>:指定报告的标题。-f 或 --force:强制重新生成报告,覆盖已存在的报告文件。--ignore <regexp>:忽略与指定正则表达式匹配的文件。--exclude <regexp>:排除与指定正则表达式匹配的文件。--no-ansi:禁用ANSI转义序列,不使用彩色输出。-q 或 --quiet:静默模式,只输出错误消息。2.3 质量检测 由于这两个软件都无法自动创建目录,因此需要手动创建输出目录:
对于单个文件,使用fastqc进行分析,如:
1 fastqc -o result -f fastq -t 8 raw_data/H1_1.fq.gz
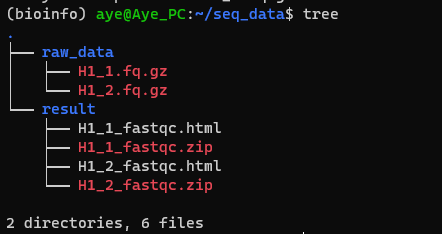
即可得到分析结果:
批量处理一个文件夹下的数据:
1 2 cd raw_datals *.gz |xargs fastqc -o ../result/ -t 8
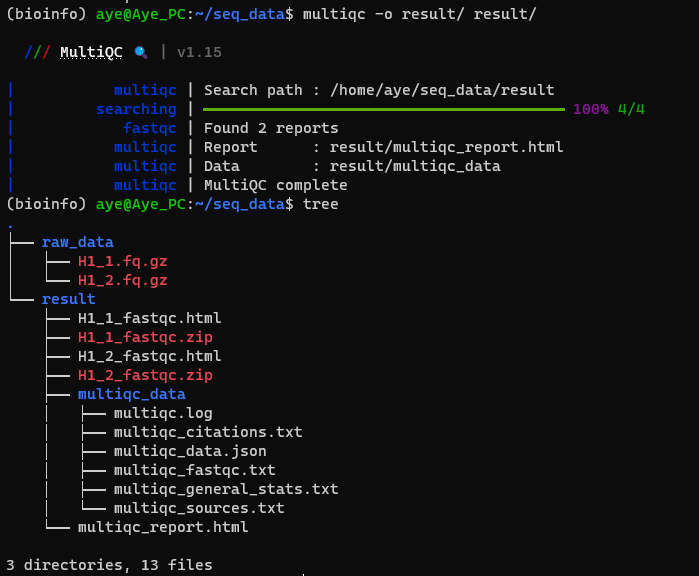
同时,可以使用MultiQC对多个数据文件进行整合:
1 multiqc -o result/ result/
三、数据清洗 3.1 软件安装 数据清洗使用的软件为Trim Galore和fastp,它前置依赖Cutadapt和FastQC
1 conda install cutadapt trim-galore fastp
3.2 参数含义 Trim Galore --quality:指定去除低质量reads的阈值,默认为20。 作用:去除质量低于指定阈值的reads--length:指定去除短reads的长度阈值,默认为20。 作用:去除长度低于指定阈值的reads--stringency:指定adapter剪切的严格程度,默认为1。 作用:调整adapter剪切的严格程度,值越高表示更严格的剪切--paired:指定输入的测序数据是否为配对的,默认为单端测序。 作用:指定处理的测序数据是否为配对的,以决定是否进行配对数据处理--phred33::选择phred33或者phred64,表示测序平台使用的Phred quality score--fastqc:生成每个输入文件的质量评估报告,同时内部调用fastqc软件。 作用:生成测序数据的质量评估报告,以便进行质量控制--fastqc_args "<ARGS>" fastqc的参数--gzip:指定输出文件是否进行压缩,默认为否。 作用:选择是否对输出文件进行压缩,可以减小文件大小--cores:指定使用的CPU核心数,默认为1。 作用:指定trim-galore使用的CPU核心数,用于加速处理速度--output_dir:输入目录。需要提前建立目录,否则运行会报错fastp -i, --in1:输入read1-o, --out1:输出read1-I, --in2:输入read2-O, --out2:输出read2-A, --disable_ adpter_ trimming:不过滤接头序列,默认过滤-f, --trim_ front1:去掉read1头部的几bp序列 ,默认为0-t, --trim _tail1:去掉read1尾部的几bp序列,默认为0-F, --trim_ front2:去掉read2头部的几bp序列,默认为0-T, --trim_ front2:去掉read2尾部的几bp序列,默认为0-q,--qualified_ quality_phred:质量值低于q的碱基将被过滤,默认为15-I, --length_ required:长度低于l的序列将被过滤,默认为15-n, --n_ base_ limit:序列中含N碱基多余n个将被过滤,默认为5-5,-3:开启滑窗质量裁剪-W:滑动窗口大小,默认4-M:滑窗裁剪平均质量,默认20-j, --json:生成可读的json文件-h, --html:生成html质控报告3.3 清洗 使用Trim Galore 1 2 mkdir clean_datamkdir clean_result
对于单个文件:
1 trim_galore --paired --cores 2 --phred33 --length 35 --stringency 1 --quality 25 --gzip --fastqc_args "-o trim_result/ -f fastq -t 8" --output_dir after_trim/ raw_data/H1_1.fq.gz raw_data/H1_2.fq.gz
批量处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 mkdir clean_datamkdir clean_resultls raw_data/*_1.fq.gz > 1ls raw_data/*_2.fq.gz > 2paste 1 2 >configcat config | while read id do $id )${arr[0]} ${arr[1]} "-o clean_result/ -f fastq -t 8" --output_dir clean_data/ $fq1 $fq2 done rm 1rm 2rm configecho "done"
批处理执行完之后即可得到清洗后的数据和报告:
使用fastp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 rm -rf clean_data clean_reportmkdir clean_datamkdir clean_reportcd raw_data/ls *_1.fq.gz > 1ls *_2.fq.gz > 2paste 1 2 >configcat config | while read id do $id )${arr[0]} ${arr[1]} echo "$fq1 " | sed 's/.fq.gz/_clean.fq.gz/' )echo "$fq2 " | sed 's/.fq.gz/_clean.fq.gz/' )$fq1 -o ../clean_data/$fq1_clean -I $fq2 -O ../clean_data/$fq2_clean -q 25 -l 35 --thread=8 -5 -3done rm 1 2 configcd ../clean_datals *_clean.fq.gz |xargs fastqc -o ../clean_report/ -t 8cd ..echo "done"
四、上游数据的比对计数 4.1 软件安装 hisat2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 sudo apt-get updatecd samtools-1.18
featureCounts 1 2 3 wget https://zenlayer.dl.sourceforge.net/project/subread/subread-2.0.6/subread-2.0.6-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz
在最下面添加一行:
1 export PATH="/home/aye/subread-2.0.6-Linux-x86_64/bin:$PATH "
使更改生效:
4.2 参数含义 hisat2 -x:参考基因组索引文件的前缀。注意最后是/genome-1:双端测序结果的第一个文件。若有多组数据,使用逗号将文件分隔。Reads的长度可以不一致-2:双端测序结果的第二个文件。 若有多组数据,使用逗号将文件分隔,并且文件顺序要和-1参数对应。Reads的长度可以不一致-S:指定输出的SAM文件。-t:输出time-p:线程使用设置-U:单端数据文件。若有多组数据,使用逗号将文件分隔。可以和-1、 -2参数同时使用。 Reads的长度可以不一致--sra-acc:输入SRA登录号, 比如SRR353653, SRR353654。多组数据之间使用逗号分隔。HISAT将自动下载并识别数据类型,进行比对view:用于将sam文件转化为bam文件-b:该参数设置输出 BAM 格式,默认下输出是 SAM 格式文件-h:默认下输出的 sam 格式文件不带 header,该参数设定输出sam文件时带 header 信息-H:仅仅输出文件的头文件-S:默认下输入是 BAM 文件,若是输入是 SAM 文件,则最好加该参数,否则有时候会报错。-u:该参数的使用需要有-b参数,能节约时间,但是需要更多磁盘空间。-c:仅输出匹配的统计记录-L:仅包括和bed文件存在overlap的reads-o:输出文件的名称-F:过滤flag,仅输出指定FLAG值的序列-q:比对的最低质量值,一般认为20就为unique比对了,可以结合上述-bF参数使用使用提取特定的比对结果-@:指使用的线程数sort:对bam文件进行排序-n:设定排序方式按short reads的ID排序。默认下是按序列在fasta文件中的顺序(即header)和序列从左往右的位点排序。-m INT:设置每个线程的最大内存,单位可以是K/M/G,默认是 768M。对于处理大数据时,如果内存够用,则设置大点的值,以节约时间。-t TAG:按照TAG值排序-o FILE:输出到文件中,加文件名index:建立索引,并生成bai文件flagstat:输出比对统计结果featureCounts -a:指定注释文件
-o:指定输出文件
-p:设置此参数后,使用fragments (或 templates)代替reads计数。只对paired-end reads有效
-t:指定GTF注释文件中的feature类型。默认:exon
exon:外显子,基因组中包含的编码序列片段。
CDS (Coding Sequence):编码序列,用于描述外显子中编码蛋白质的部分。
start_codon:起始密码子,表示编码蛋白质的起始位置。
stop_codon:终止密码子,表示编码蛋白质的终止位置。
UTR (Untranslated Region):未翻译区域,编码序列中没有被翻译为蛋白质的区域。
transcript:转录本,表示基因的一个转录过程,包含一系列的外显子。
gene:基因,包含一个或多个转录本。
tRNA:转移RNA,一类用于将氨基酸传递到翻译中的蛋白质合成过程的分子。
rRNA:核糖体RNA,一类参与蛋白质合成的RNA分子。
snoRNA:小核仁RNA,参与核仁中的RNA加工和修饰。
miRNA:微RNA,一类通过调控基因表达参与调节细胞内RNA稳定性的小分子RNA。
snRNA:小核RNA,参与剪接反应和转录调控。
-g:指定GTF注释文件中属性的类型。默认:gene_id
gene_id:基因的唯一标识符。
transcript_id:转录本的唯一标识符。
gene_name:基因的名称。
transcript_name:转录本的名称。
exon_number:外显子的编号。
exon_id:外显子的唯一标识符。
protein_id:蛋白质序列的唯一标识符。
gene_biotype:基因的生物类型,例如编码蛋白质的基因、非编码RNA基因等。
transcript_biotype:转录本的生物类型,例如编码蛋白质的转录本、非编码RNA转录本等。
gene_source:基因注释来源,表示该基因的来源数据库或参考序列。
transcript_source:转录本注释来源,表示该转录本的来源数据库或参考序列。
gene_symbol:基因的符号名称。
transcript_symbol:转录本的符号名称。
-f:在feature水平计数 (如对外显子计数)
-O:统计所有重叠的的meta-features的reads
-C:对于比对到不同染色体或相同染色体的不同链的read对,不进行计数
-T:使用线程
4.3 数据处理 get sam file 首先使用hisat2比对基因组得到sam文件,这里需要先下载参考基因组,因为我这里用的是人类细胞,所以使用hg38:
1 2 3 4 5 cd mkdir -p reference/index/hisatcd reference/index/hisat/
这玩意很大,下不下来也可以考虑使用别的方法下载后上传到服务器
下载并解压后文件如下:
接下来比对基因组
1 hisat2 --dta -t -x ../../reference/index/hisat/hg38/genome -1 H1_1_clean.fq.gz -2 H1_2_clean.fq.gz -p 4 -S hisat2_hg38data/H1.sam
这里genome是参考基因组文件的前缀
sam to bam 之后,使用samtools进行进一步操作,首先是将sam文件转化为bam文件:
1 samtools view -@ 8 -bS -o hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.bam hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.sam
sort and index 接下来对bam进行排序:
1 samtools sort -@ 8 -o hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.sort.bam hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.bam
之后对使用排序好的文件建立索引
1 samtools index hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.sort.bam
最后,将比对结果输入到文件中保存:
1 samtools flagstat -@ 8 -O json hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.sort.bam > hisat2_hg38data/H1_1.sort.flagsata
count table 使用featureCounts获得counts.txt:
1 featureCounts -a ../reference/gtf/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.110.chr.gtf.gz -g gene_id -t gene -O -p -T 8 -C -o counts/counts.txt hisat2_hg38data/*.sort.bam
批量处理: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 rm -rf hisat2_hg38data/mkdir hisat2_hg38datacd clean_data/ls *1_clean.fq.gz > 1ls *2_clean.fq.gz > 2paste 1 2 >configcat config | while read id do $id )${arr[0]} ${arr[1]} echo "$fq1 " | sed 's/_1_clean.fq.gz/.sam/' )echo "hisat2 --dta -t -x ../../reference/index/hisat/hg38/genome -1 $fq1 -2 $fq2 -p 8 -S ../hisat2_hg38data/$output " $fq1 -2 $fq2 -p 8 -S ../hisat2_hg38data/$output done rm 1 2 configcd ../hisat2_hg38dataecho "start sam to bam and sorting..." ls *.sam | xargs -I {} sh -c 'samtools view -@ 8 -bS {} | samtools sort -@ 8 -o $(basename {} .sam).sort.bam' echo "done, removing sam file..." ls *.sam | xargs rm echo "done" echo "start indexing..." ls *.sort.bam | xargs samtools index -M echo "done" echo "saving to flagsata..." ls *.sort.bam | xargs -I {} sh -c 'samtools flagstat -@ 8 {} > $(basename {} .bam).flagstat' echo "done" cd ..rm -rf countsmkdir counts
4.4 结果解读 hisat2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 19429766 reads; of these: times times times ; of these: times concordantly or discordantly; of these: times times
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 51231959 + 0 in total (QC-passed reads + QC-failed reads) in sequencing
五、表达水平计算 经由上一步,得到了counts.txt,接下来就基于它进行进一步的计算。
虽然主流都是R语言,不过我比较属性python,反正都是大数据处理,没差别(
5.1 count的结构 我这里根据上面的参数,生成的count结构如下所示:
Geneid:基因的唯一标识符 Chr:基因所在的染色体 Start:基因在染色体上的起始位置 End:基因在染色体上的终止位置 Strand:基因在染色体上的定向,正义链为"+", 反义链为"-" Length:基因的长度,单位为碱基 H1、H2:基因在样品中的表达量 5.2 RPKM、FPKM和TPM 计算步骤 RPKM和FPKM计算方法一致,区别仅在于原始数据是否使用双端测序得来,其公式为:
\[ \begin{align} RPKM(x) &= \frac{Reads\ per\ transcription}{\frac{totla\ reads}{10^6} \times \frac{transcription\ length}{1000}}\\ &= \frac{10^9 \times C_x}{R \times L_x} \end{align} \]
具体而言,可以分成三步:
对read count求和,并除以1000000 将每一个read count除以上面的结果,得到RPM(read per million) 将RPM除以length再乘以1000,得到RPKM TPM类似,其计算公式为:
\[ TPM(X)=\frac{C_x \times r \times 10^6}{L_x \times T} \]
具体步骤也可以分为三步:
将每一个read count除以length,乘以1000,得到RPK 对RPK求和并除以1000000 再用RPK除以上面的结果,得到TPM 程序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as np'counts.txt' , sep='\t' )print (counts_df.columns)len (counts_df) - 1 print (f'表达的基因数为:{express_num} ' )'H1' ] > 10 ) | (counts_df['H2' ] > 10 )).sum ()print (f"有{count_10} 个基因read count > 10。" )'Geneid' ] = counts_df['Geneid' ]'H1' ] / (counts_df['H1' ].sum () / 10 ** 9 )'H2' ] / (counts_df['H2' ].sum () / 10 ** 9 )'H1' ] = (FMP1 / counts_df['Length' ]) * 10 ** 3 'H2' ] = (FMP2 / counts_df['Length' ]) * 10 ** 3 'fpkm.csv' , sep='\t' , index=False )'Geneid' ] = counts_df['Geneid' ]'H1' ] / counts_df['Length' ]) * 10 ** 3 'H2' ] / counts_df['Length' ]) * 10 ** 3 'H1' ] = RPK1 / (sum (RPK1) / 10 ** 6 )'H2' ] = RPK2 / (sum (RPK2) / 10 ** 6 )'tpm.csv' , sep='\t' , index=False )'H1' : np.log2(FPKM['H1' ] + 1 ),'H2' : np.log2(FPKM['H2' ] + 1 )}0 , np.nan)'density' )'log2(FPKM+1)' )'Density' )'Density of FPKM' )'H1' : np.log2(TPM['H1' ] + 1 ),'H2' : np.log2(TPM['H2' ] + 1 )}0 , np.nan)'density' )'log2(TPM+1)' )'Density' )'Density of TPM' )print ('done' )
参考